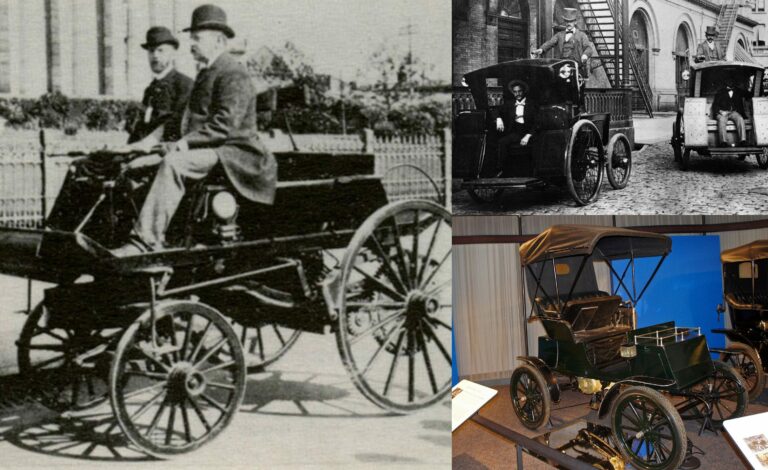
Early Beginnings of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars dates back to the 1830s when Scotland’s Robert Anderson created a motorized carriage between 1832 and 1839. Although the batteries were not rechargeable at the time, this marked the beginning of electric vehicle development. Another Scot, Robert Davidson, built an electric locomotive in 1837, which could go 1.5 miles at 4 mph towing six tons.
The Emergence of Rechargeable Batteries
The invention of rechargeable batteries in 1859 made electric cars more viable. Thomas Parker helped deploy electric-powered trams and built prototype electric cars in England around 1884. William Morrison, a Scotland-born chemist living in Des Moines, Iowa, applied for a patent on an electric carriage in 1890, which was showcased in a city parade in 1888.
Early Commercial Electric Vehicles
The first commercially viable EV effort was the Electrobat, developed by Philadelphians Pedro Salom and Henry G. Morris. They adapted technology from battery-electric street cars and boats and received a patent in 1894. Their company eventually became part of the Electric Vehicle Company (EVC), which operated over 600 electric cabs in New York by the early 1900s.
Electric Cars in the Early 20th Century
Electric cars proved their mettle in early motorsports, with Belgian Camille Jenatzy breaking the 100-km/h barrier in 1899. Brands like Oldsmobile, Studebaker, and even Thomas Edison experimented with electric vehicles. However, the rise of gasoline-powered cars, particularly Henry Ford’s Model T, led to a decline in electric car popularity due to their higher cost and limited range.
Mid-20th Century Revival
Interest in electric cars revived during the 1960s and 1970s, driven by concerns over air pollution and oil shortages. General Motors developed the Electrovair II in 1966, featuring advanced silver-zinc batteries. The Henney Kilowatt, produced from 1959 to 1961, was another attempt at a modern electric car.
Modern Electric Vehicles
The modern era of electric cars began with the General Motors EV1 in the late 1990s, followed by the Tesla Roadster in 2008. Tesla’s success paved the way for other manufacturers to develop their own electric vehicles, such as the Nissan Leaf and Chevrolet Bolt. Today, electric cars are recognized as a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, offering improved performance, reduced environmental impact, and lower operating costs.