California Leads Nation with Over 178,000 EV Chargers
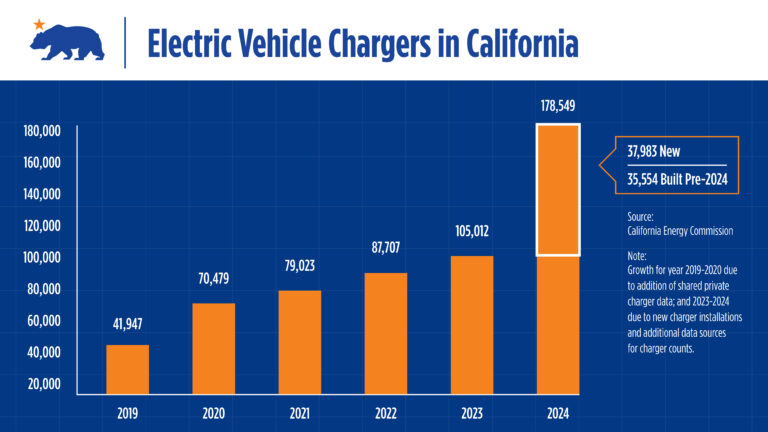
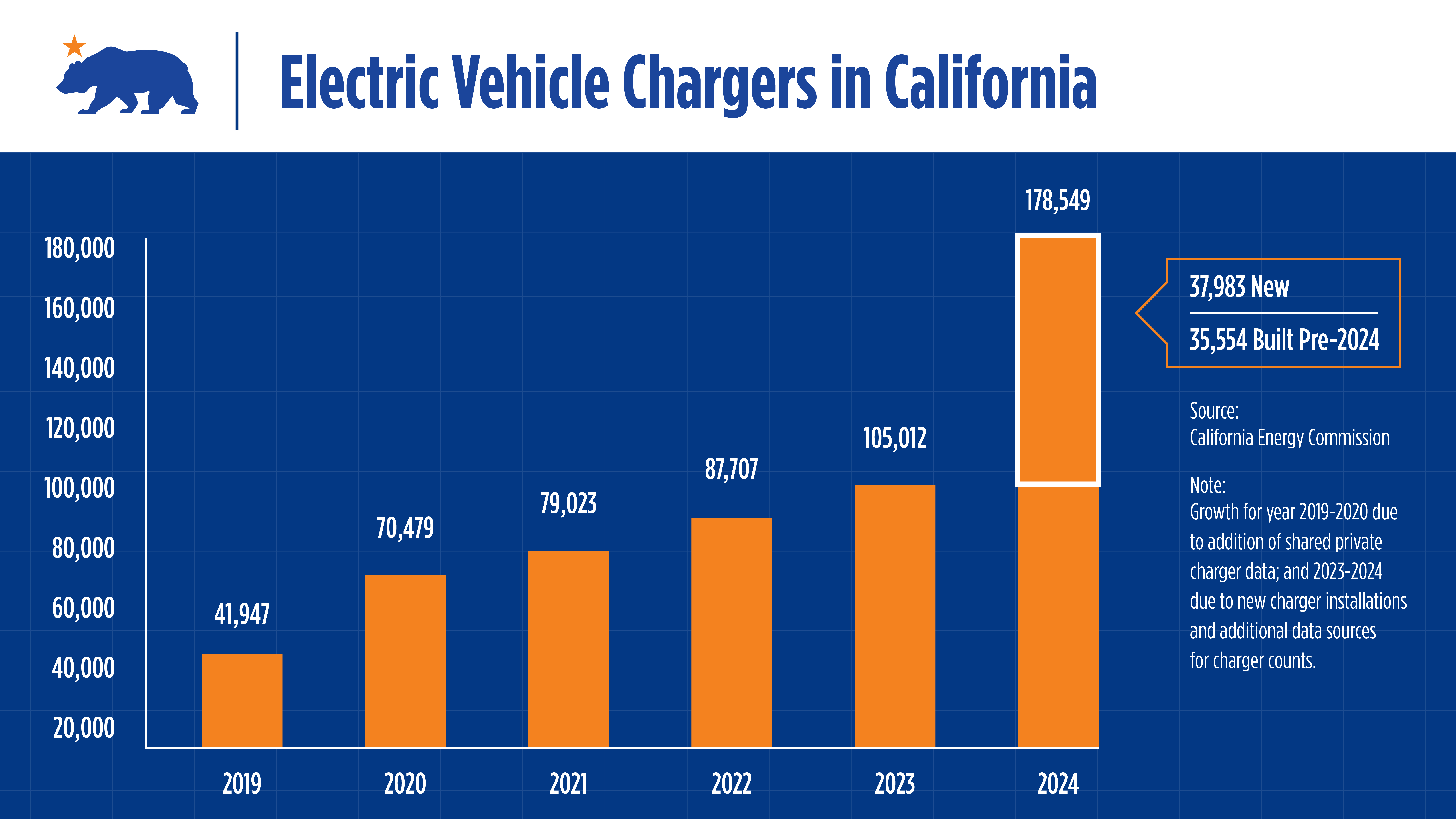
SACRAMENTO — California continues to expand its electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure at a rapid pace, solidifying its position as a leader in the clean transportation sector. The California Energy Commission (CEC) announced today that the state’s public and shared private EV charger count has reached 178,549. This number surpasses the estimated 120,000 gasoline nozzles across California.
Of the total, 162,178 are Level 2 chargers, and 16,971 are fast chargers. In addition to the public network, the CEC estimates over 700,000 Level 2 chargers are installed in single-family homes across the state.
“The California EV driver experience is getting better by the day,” said CEC Chair David Hochschild. “The state will continue to heavily invest in EV infrastructure, with particular emphasis in hard-to-reach areas, making these vehicles an easy choice for new car buyers.”
Billions Invested in EV Infrastructure
California is committed to supporting clean transportation goals and continues to invest heavily in EV infrastructure, with billions of dollars allocated to expanding the charging and hydrogen network. This includes projects like the Fast Charge California Project, which is part of the California Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Project (CALeVIP). The project will award $55 million to install fast-charging stations at businesses and public locations.
Furthermore, grants and rebates are available for low-income Californians to promote EV adoption.
Improving Data Collection for a Better Charging Experience
The CEC is working to improve the EV driver experience through better data collection. This effort helps understand charger demand and track the state’s progress in meeting ZEV goals.
The updated charger totals announced today reflect efforts to improve data collection using additional sources to track operational chargers. In 2024, 37,983 new chargers were installed, while an additional 35,554 chargers installed before 2024 were identified through new data sources.
Building a Comprehensive Charging Network
State agencies are focused on accelerating charger deployment, streamlining regulations, establishing guidelines, planning for increased grid demand, and electrifying charging stations through local utilities. Actions include:
- Gathering better data on EV charger counts.
- Prioritizing shovel-ready projects.
- Developing a comprehensive infrastructure plan.
- Establishing charger reliability standards.
California is also collaborating with private sector partners for EV charging infrastructure expansion. Reflecting the strength of the ZEV market, one in four Californians have chosen zero-emission models over gasoline-powered vehicles in the past two years. According to the California Air Resources Board, 30% of new ZEVs sold in the U.S. are sold in California.