Mitsubishi is teaming up with Ample and Yamato Transports to introduce a groundbreaking battery swap network for electric vehicles in Japan, extending its application beyond passenger cars to include commercial trucks. The initiative, backed by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government’s ‘Technology Development Support Project for Promoting New Energy,’ aims to revolutionize the transport industry’s shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) by addressing range anxiety and charging downtime.
The Battery Swap Solution
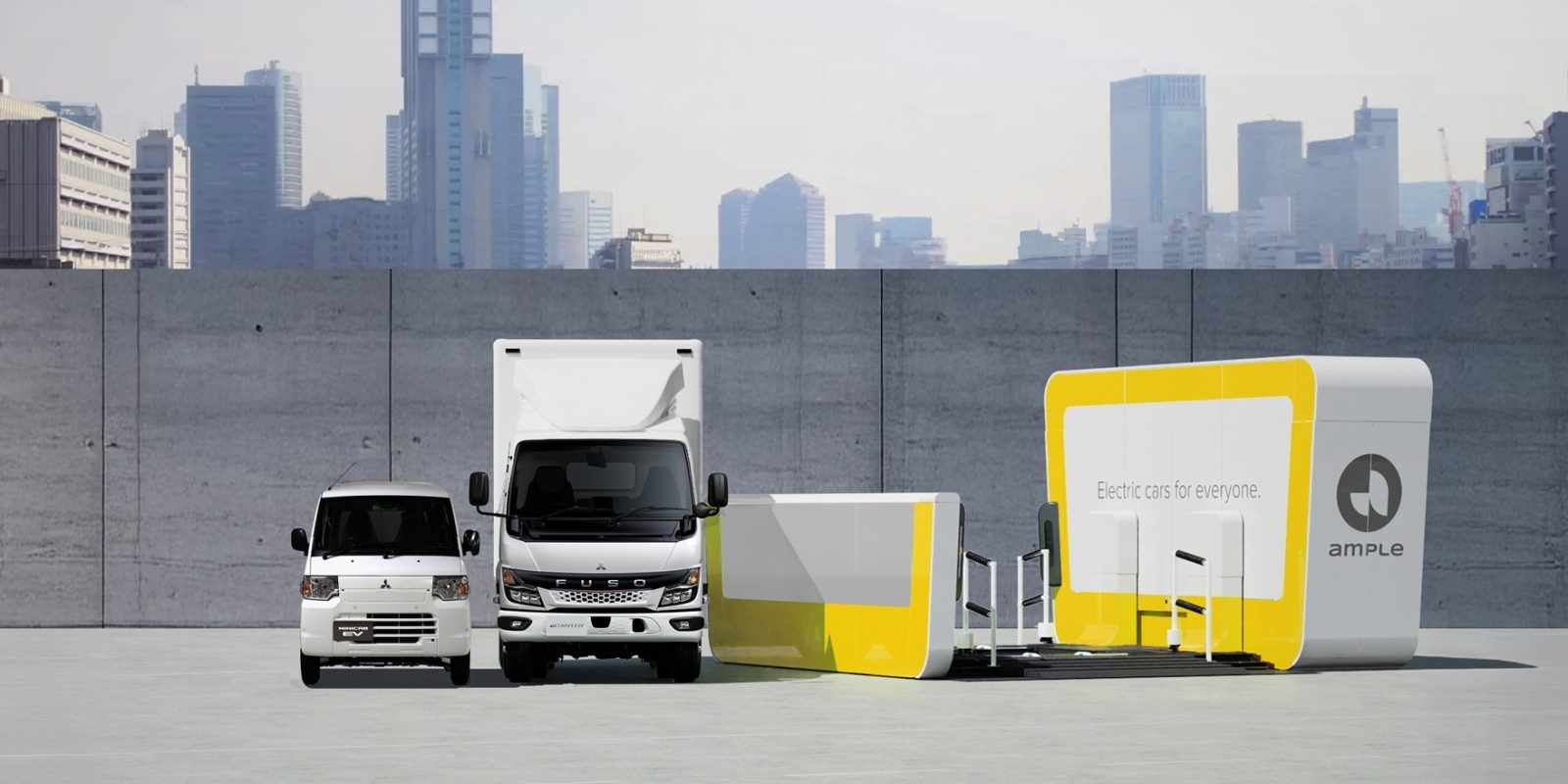
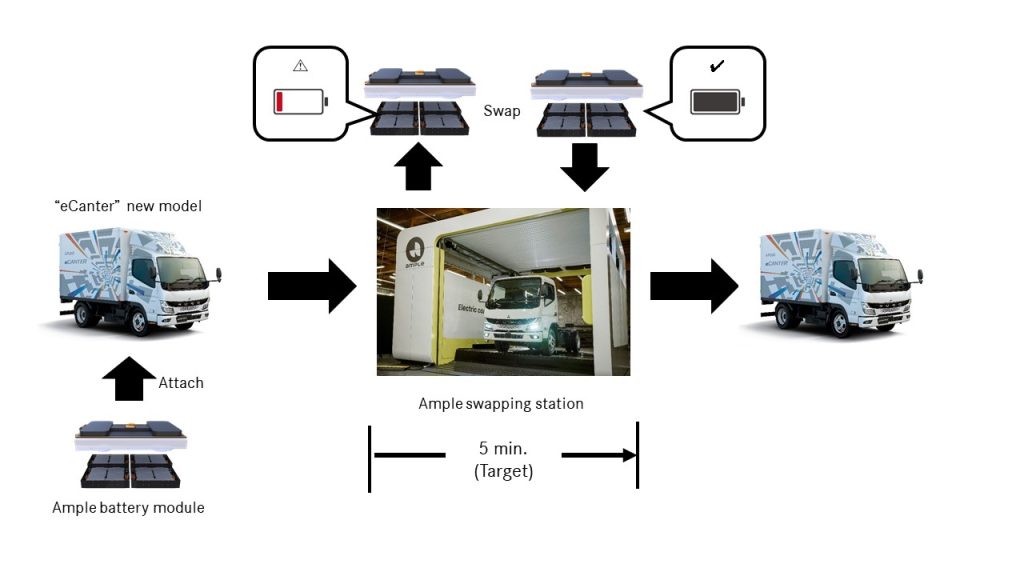
The pilot program involves deploying over 150 battery-swappable commercial electric vehicles and 14 modular battery swapping stations across Tokyo. This innovative technology allows for a full charge in just a few minutes, significantly reducing vehicle downtime. For instance, the Mitsubishi eCanter typically requires a full night of AC charging or at least an hour or two on DC charging. The battery swap technology circumvents this issue, supporting vehicle uptime and making electric trucks more viable for commercial fleets.
How It Works
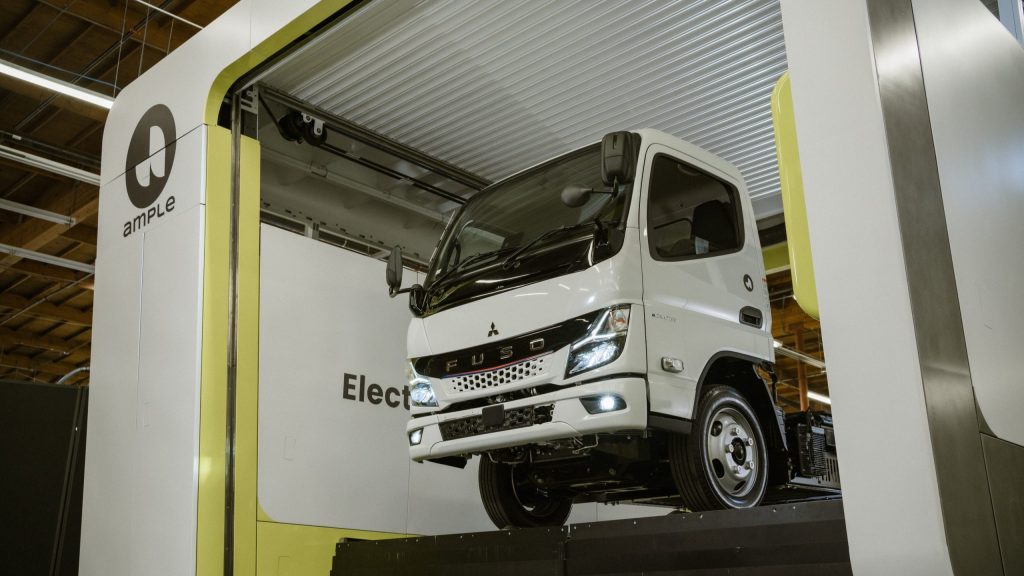
The process involves swapping the depleted battery pack with a fully charged one in approximately 100 seconds, a time comparable to or even quicker than refueling a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle. This technology is particularly beneficial for commercial trucks like the eCanter, which serve various roles including municipal waste collection and regional delivery support.
Benefits for Commercial Fleets
Electrifying commercial truck fleets is a crucial step in decarbonizing city truck fleets globally. The battery swap technology eliminates the corporate fear of EV charging, making electric trucks an even more attractive option for densely packed city streets. The pilot program, which includes testing swappable EVs for delivery operations on both eCanter light-duty trucks and Mitsubishi Minicab kei-class electric vans, is expected to showcase the efficacy of ‘five-minute charging’ technology.
Broader Implications
Beyond promoting the EV shift, the initiative also aims to create a depository of stored energy that can be deployed to the grid during natural disasters, a concept Mitsubishi has been exploring in Japan for years. This dual benefit positions the battery swap network as a significant step towards both sustainable transportation and energy resilience.