Trump’s Re-election Could Significantly Damage EV Adoption, Study Finds
The potential re-election of Donald J. Trump poses a considerable threat to the ongoing transition to electrified vehicles (EVs) in the United States, according to a recent study by the REPEAT Project. The analysis explores possible consequences of Trump’s previously stated intentions to dismantle federal regulations targeting greenhouse gas emissions from cars and trucks, eliminate EV purchase incentives, and redirect federal grant programs supporting EV charging infrastructure.

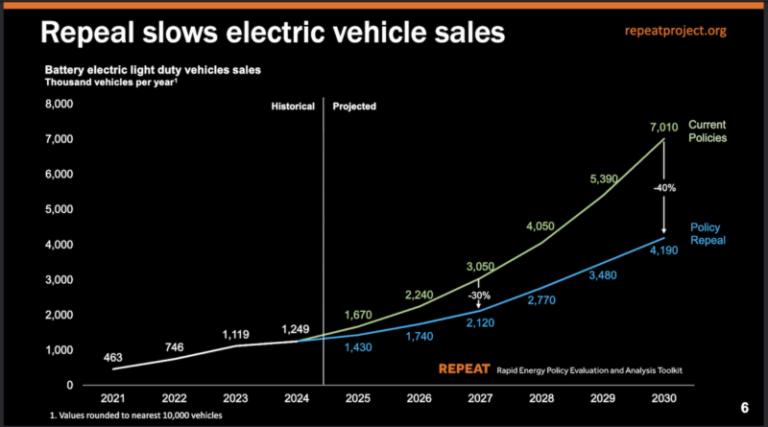
This image shows projected drops in EV sales and manufacturing due to the suggested policy changes.
Key Findings
The REPEAT Project’s study, which assesses the broad economic effects of possible shifts in federal energy and climate policies, reveals potential downturns in the U.S. automotive industry:
- Reduced EV Sales: Repealing EPA tailpipe emissions regulations and federal clean vehicle tax credits could lead to a 30% drop in battery electric vehicle (BEV) sales in 2027 and a 40% drop by 2030 compared to maintaining existing policies.
- Declining Market Share: The share of BEVs in new light vehicle sales could decrease from roughly 18% to 13% in 2026, and from 40% to 24% in 2030.
- Fewer EVs on the Road: By 2030, the U.S. could have 8.3 million fewer EVs and plug-in hybrids operating on its roads.
- Threatened Manufacturing: Planned expansions and developments in the U.S. electric vehicle assembly sector could be severely affected, with up to 100% of planned construction and half of existing assembly capacity potentially at risk of cancellation or closure.
- Impact on Battery Production: A significant portion of battery cell manufacturing capacity could become redundant. Between 29% and 72% of battery cell manufacturing capacity currently operational or set to come online by the close of 2025 could become unnecessary, potentially leading to closures, in addition to 100% of planned facilities.
The study also indicates that there could be further, though currently unquantified, impacts on the U.S. materials, parts, and component suppliers involved in EV and battery assembly.
About the Study
The research was conducted by the REPEAT Project, offering an in-depth look at how these prospective policy changes could influence the U.S. vehicle market and their ramifications for domestic battery and EV manufacturing. The study’s lead researcher is Jesse Jenkins.
Source: Jenkins, J. (2025). Potential Impacts of Electric Vehicle Tax Credit Repeal on US Vehicle Market and Manufacturing. REPEAT Project. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15001499